Configuration¶
SMUI may be configured by passing environment variables to its docker container. The following section describes all configuration parameters.
Note
Environment variables are the preferred way to configure your
production environment. During development (i.e. outside a docker
environment) it is possible to use a local smui-dev.conf file
(see the development setup documentation).
The following sections describe application configs in more detail.
Basic settings¶
The following settings can (and should) be overwritten on
application.conf in your own smui-prod.conf or in your deployment,
using environment variables:
Config key |
Environment variable |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
JDBC database driver |
|
|
|
Database host and optional connection parameters (JDBC connection string). |
|
|
|
Database user |
|
|
|
Database password |
|
|
|
Path to temp file (i.e. where to output the generated |
|
|
|
LIVE |
|
|
|
Only necessary for git deployment (see git deployment documentation). |
|
|
|
Bare filename of the common |
|
|
|
Virtual local Solr instance. WARNING: Deprecated as of v3.4, will be replaced soon. |
|
|
|
Encryption key for server/client communication (Play 2.6 standard). This positively needs to be set to a high-entropy value in production environments. |
WARNING: insecure default. |
SMUI with SQLite (in a Docker setup)¶
To use SMUI with SQLite in a Docker setup, you need to:
Make sure the SQLite database is read/write mounted to the SMUI Docker container.
Use the correct JDBC driver for SQLite with a URL pointing to the mounted database file, e.g.
NOTE: Play is not good in handling SQLite out-of-the-box. We need to disable locks for Play database evolutions. A custom-application.conf is therefore also needed. It contains:
include "application.conf"
play.evolutions.useLocks=false
This is the complete command to run a SMUI container with a SQLite DB and the necessary custom-application.conf (NOTE: environment variables for the CMD must be set in the environment starting SMUI).
docker run -p 9000:9000 \
--mount type=bind,source=/PATH/TO/local_sqlite_smui.db,target=/smui/smui.db \
--mount type=bind,source=/PATH/TO/custom-application.conf,target=/smui/conf/custom-application.conf \
-e SMUI_DB_JDBC_DRIVER=org.sqlite.JDBC \
-e SMUI_DB_URL=jdbc:sqlite:/smui/smui.db \
querqy/smui \
java -Dpidfile.path=$SMUI_CONF_PID_PATH -Dlogback.configurationFile=$SMUI_CONF_LOGBACK_XML_PATH -Dhttp.port=$SMUI_CONF_HTTP_PORT -Dconfig.file="/smui/conf/custom-application.conf" -jar /smui/search-management-ui-assembly-$SMUI_VERSION.jar
Advanced configuration¶
The following sections describe the configuration of:
application behaviour / feature toggles (e.g. rule tagging)
details and options for the deployment (of Querqy’s
rules.txtfile)authentication
The following tables only list the config keys as defined in the SMUI application.conf file.
See the file for the mappings of config keys to environment variables
(e.g. SMUI_DB_JDBC_DRIVER environment variable sets db.default.driver).
Feature toggles¶
The following settings are optional and define the general SMUI behaviour:
Config key |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
Show UP(+++) fields instead of separated rule and intensity fields. |
|
|
Offer a separated “Solr Field” input to the user (UP/DOWN, FILTER). |
|
|
With every exported search input, add an additional |
|
|
Separate decompound synonyms ( |
|
|
Path to productive querqy |
Example content, that needs to be adjusted, if split for decompound rules.txt has been activated. |
|
Make separated deployments PRELIVE vs. LIVE possible (and display a button for that on the frontend). |
|
|
PRELIVE |
|
|
Host and port (e.g. |
Empty. In case core reload on PRELIVE deployments should be triggered, this needs to be set. |
|
Separate decompound synonyms for PRELIVE (see above). |
|
|
If set to |
|
|
Path to an optional custom script (see above). |
Example content, that needs to be adjusted, if a custom deployment script is activated. |
|
Should tagging feature be activated. |
|
|
Path to optional file, that provides pre-defined rule tags (see “Configure predefined rule tags”). |
|
|
Activate spelling items: Add spelling items to maintain common misspellings using the Querqy replace rewriter. The spelling items are exported in a separate replace_rules.txt that is uploaded to Solr. |
|
|
Activate list limitation: Limits the list of visible items to the configured number and shows toggle button (“show more/less”). Set value to -1 to deactivate list limitation. |
|
|
Path to temp file (when |
|
|
|
|
|
PRELIVE |
|
|
WARNING: Deprecated as of v3.14, will be replaced soon (see github.com comment on PR#83). Default username for being displayed on the frontend, if no username is available (e.g. for event history). |
|
|
Persist an event history for all updates to the search management configuration, and provide an activity log for the search manager. WARNING: If this setting is changed over time (especially from |
|
|
Provide custom mapping / step sizes for UP/DOWN boosting/penalising values as JSON (used, if |
|
|
Target environment configuration (e.g. for preview links). See below for details. |
Empty target environment. NOTE: There will come a dummy config showcasing this feature withz upcoming (majo) releases. |
|
Enable reporting of rules usage. |
No rules usage report. |
Note
The above described feature toggles are passed to SMUI’s docker container using according environment variables. The mappings can be found in the application.conf.
Custom UP/DOWN dropdown mappings (optional)¶
SMUI makes life easier when dealing with UP/DOWN boosting/penalising intensities.
It translates raw values passed to querqy to a more comprehensible format to
the search manager working with +++ and --- on the frontend.
By default, a typical intensity range from 500 to 5 is covered, which
should work with most search engine’s (e.g. Solr) schema configurations and the according querqy setup.
However, if SMUI’s default does not match the specific needs, the default can be adjusted.
This can be achieved by passing a JSON object describing the desired custom UP/DOWN dropdown
mappings to SMUI while using the toggle.ui-concept.custom.up-down-dropdown-mappings configuration.
The JSON is passed as an escaped string, which is then validated by SMUI.
Note: If for any reason your custom mappings do not apply, check SMUI’s (error) logs, as it is likely, that the validation yielded an error.
Example configuration setting:
toggle.ui-concept.custom.up-down-dropdown-mappings="[{\"displayName\":\"UP(+++++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":750},{\"displayName\":\"UP(++++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":100},{\"displayName\":\"UP(+++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":50},{\"displayName\":\"UP(++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":10},{\"displayName\":\"UP(+)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\": 5},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(-)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 5},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(--)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 10},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(---)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 50},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(----)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 100},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(-----)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 750}]"
Note that all attribute/value quotation marks in the JSON string need to be escaped. The equivalent docker startup argument would be (command line):
docker run \
...
-e SMUI_CUSTOM_UPDOWN_MAPPINGS="[{\"displayName\":\"UP(+++++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":750},{\"displayName\":\"UP(++++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":100},{\"displayName\":\"UP(+++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":50},{\"displayName\":\"UP(++)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\":10},{\"displayName\":\"UP(+)\",\"upDownType\":0,\"boostMalusValue\": 5},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(-)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 5},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(--)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 10},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(---)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 50},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(----)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 100},{\"displayName\":\"DOWN(-----)\",\"upDownType\":1,\"boostMalusValue\": 750}]"
...
Preview search queries (optional)¶
Preview links can be configured using the smui.target-environment.config in your custom application.conf.
Here is an example of a multi tenant, multi language preview configuration.
NOTE: The JSON structure is encoded into the HOCON syntax (used by Play / typesafe) as a multiline string:
smui.target-environment.config="""{
"LIVE": {
"de": [
{
"rulesCollection": "MainTenantDE",
"tenantTag": null,
"previewUrlTemplate": "https://www.example.com/de/main-tenant/search?query=$QUERY"
}, {
"rulesCollection": "AlternativeTenantDE",
"tenantTag": "tenant:ALTERNATIVE",
"previewUrlTemplate": "https://www.example.com/de/alternative-tenant/search?query=$QUERY"
}
],
"fr": [
{
"rulesCollection": "MainTenantFR",
"tenantTag": null,
"previewUrlTemplate": "https://www.example.com/fr/main-tenant/search?query=$QUERY"
}, {
"rulesCollection": "AlternativeTenantFR",
"tenantTag": "tenant:ALTERNATIVE",
"previewUrlTemplate": "https://www.example.com/fr/alternative-tenant/search?query=$QUERY"
}
]
},
"PRELIVE": {
...
}
}"""
The first level of the JSON describes the deployment instance that the preview links points to.
Next is a free-definable organizational identifier - typically encoding the language. Then follows the preview link configuration itself.
Preview links are tight to a rules collection, and might be scoped to specific tenants.
The links are rendered using the magic $QUERY symbol in the URL template.
NOTE: TODO As of v3.15 this will be the designated structure for the deployment description in the future.
Authentication¶
In version 4 SMUI has dropped support for its proprietary authentication implementation and adopted the pac4j library. pac4j offers a wide range of authentication and authorization mechanisms. At the moment, only SAML authentication is provided (tested against MS Azure AD / Entra, other SAML identity providers should work) but additional authentication mechanisms can be added quickly. Please create a Github issue, a pull request, or drop us an email.
SAML Authentication¶
Enabling SAML authentication requires a few steps of preparation. We describe the steps below using Microsoft Entra (ex Azure Active Directory) as the Identity Provider (IdP).
First, create a new SMUI application in your IdP. In MS Entra this can be achieved in the Application / Enterprise Applications / New application dialogue. You will create a new “non-gallery” application.
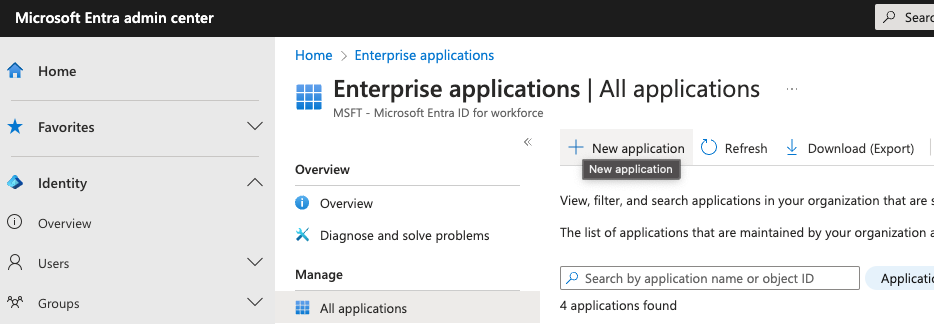
Second, enable SAML Single sign-on for SMUI. In MS Entra this is done by Selecting the SAML option in the Manage / Single sign-on menu of your newly created application.
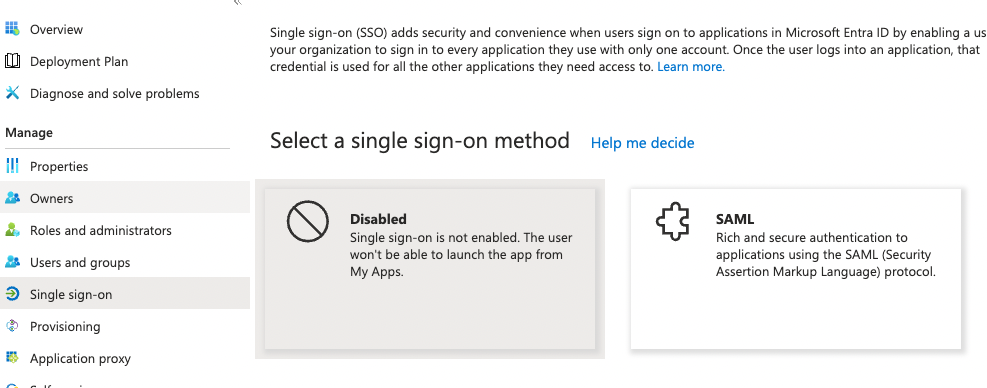
Third, assign an entity ID to your new application. This identifier is also called the Audience Restriction or Audience URI in other identity providers. In MS Entra this is configured in the Single sign-on section of your newly created application. There, the Basic SAML Configuration sub-section’s Identifier (Entity ID) entry should contain the ID. There is some recommendation to use a URI for SAML entity IDs but in general any globally unique identifier will work.
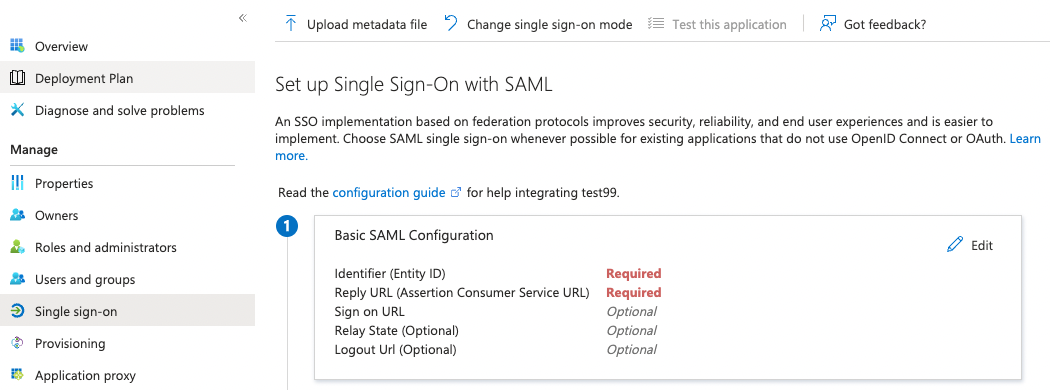
Fourth, configure your IdP to return your browser back to a SMUI callback endpoint after successful authentication. In MS Entra, this happens in the same section as above with the Reply URL (Assertion Customer Service) setting. Here you will need to use your SMUI host’s URL appended with /callback?client_name=SAML2Client. Please note, that SAML requires this to be a HTTPS URL. Example: https://smui.intranet.mycompany.com/callback?client_name=SAML2Client
Fifth, prepare the identity provider’s metadata XML. This includes required signatures and SSO URL configurations and follows a standard format. In MS Entra you can download the Federation Metadata XML in the SAML Certificates Section of the application’s Single sign-on configuration dialog. For pac4j only the Signature and IDPSSODescriptor elements in the XML are used and you would need to remove (!) additional XML RoleDescriptor elements as we had issues with pac4j complaining about unexpected elements.
Sixth, assign users and/or groups to that new application to enable your users to allow authenticating your SMUI users against this new application.
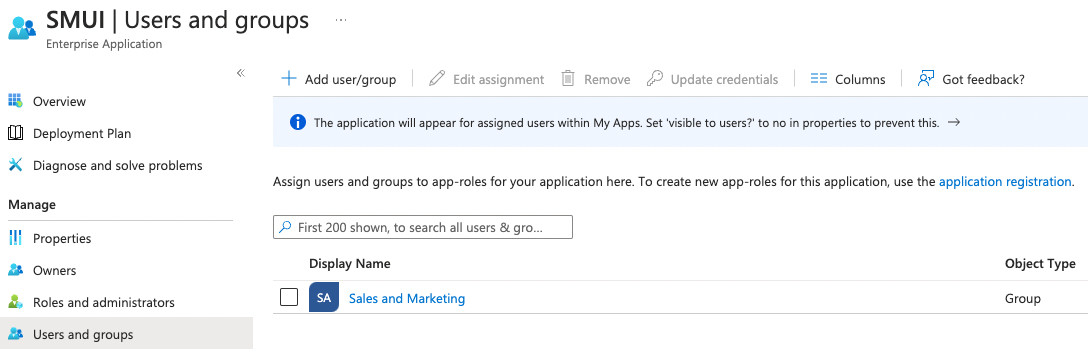
After the above steps you are able to run SMUI with enabled SAML authentication with the following environment variables:
# This triggers SMUI to use the SAML2Client
SMUI_AUTH_CLIENT=SAML2Client
# This sets the SMUI base URL, required for callbacks etc.
# Should just be the protocol+hostname+port you run SMUI on
SMUI_AUTH_BASEURL=https://<add-you-host-here>
# The SAML entity ID configured in step three above
SMUI_SAML_SERVICE_PROVIDER_ENTITY_ID=<unique-configured-id>
# Path to the identity provider metadata XML obtained in step five above
SMUI_SAML_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_METADATA_PATH=/path/to/idp.xml
# Path to a keystore for a public/private key pair that SMUI uses to sign SAML messages.
# If it does not exist it is created during SMUI startup
SMUI_SAML_KEYSTORE=/tmp/smui_saml_keystore.jks
# The password to the keystore above. It needs to match the actual keystore password
# if an existing keystore is provided, otherwise it will be the password SMUI uses
# when creating the new keystore file.
SMUI_SAML_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=keystore-password
# The password to the private key within the keystore. It needs to match the actual
# private key password if an existing keystore is provided, otherwise it will be the
# password SMUI uses when creating the new keystore file.
SMUI_SAML_PRIVATE_KEY_PASSWORD=private-key-password
# SMUI will generate an XML file for its own metadata and post that during the SAML
# authentication process. This is the path where this file will be stored. Please note,
# that you might need to manually delete this file if you change any of the above configuration.
SMUI_SAML_SERVICE_PROVIDER_METADATA_PATH=/tmp/smui_sp_metadata.xml
# SMUI will store authenticated user info in a browser cookie. You can set the maximum
# duration of this session before requiring re-authentication using this value.
SMUI_SESSION_MAXAGE=1 day
(!) NOTE: The <unique-configured-id> (for config SMUI_SAML_SERVICE_PROVIDER_ENTITY_ID) usually starts with spn: (i.e. for Microsoft Azure/IdP).
Session and Logout¶
An authenticated user will stay logged in as long as their cookie is valid (see SMUI_SESSION_MAXAGE value above).
As we currently only support external authentication there is currently no active logout implemented (any logout
would immediately redirect to the identity provider and, if the session with the identity provider still exists,
re-login the user).
Options for rules deployment¶
Deploying rules.txt via cp/scp¶
The default deployment script supports using cp or scp file transfer
as methods to deploy the rules.txt and replace_rules.txt and triggers a Solr core on the
target system, if configured accordingly. Its behaviour is controlled
using the config variables above, e.g.:
docker run \
...
-e SMUI_2SOLR_DST_CP_FILE_TO=remote_user:remote_pass@remote_host:/path/to/live/solr/defaultCore/conf/rules.txt \
-e SMUI_2SOLR_SOLR_HOST=remote_solr_host:8983 \
-e SMUI_DEPLOY_PRELIVE_FN_RULES_TXT=/mnt/prelive_solr_depl/rules.txt \
-e SMUI_DEPLOY_PRELIVE_SOLR_HOST=docker_host:8983 \
...
-v /path/to/prelive/solr/defaultCore/conf:/mnt/prelive_solr_depl
...
querqy/smui
In this particular example, the LIVE instance of Solr runs on
remote_solr_host and can be reached by remote_user on
remote_host for rules.txt deployment (NOTE: remote_host as
well as remote_solr_host might even be the same instance, but just
have differing network names). scp will be chosen by the default
deployment script. In contrast to that, the PRELIVE instance of Solr
resides on the docker_host. File deployment is ensured using an
according docker volume mount. cp will be chosen.
Note
The example above also accounts for
SMUI_TOGGLE_DEPL_DECOMPOUND_DST and
SMUI_DEPLOY_PRELIVE_FN_DECOMPOUND_TXT, when
SMUI_TOGGLE_DEPL_SPLIT_DECOMPOUND is set to true.
Note
The example above also accounts for
SMUI_2SOLR_REPLACE_RULES_DST_CP_FILE_TO and
SMUI_DEPLOY_PRELIVE_FN_REPLACE_TXT, when
SMUI_TOGGLE_SPELLING is set to true.
Deploying rules.txt to a git target¶
The SMUI docker container comes with an alternative
deployment script for deployment to git, which is located under
conf/smui2git.sh.
Note
Your rules.txt repository needs to be initialised with (at least) the empty files,
you would like to get managed by SMUI on the master branch (or branch you would like SMUI to deploy to).
The conf/smui2git.sh main deployment script uses the
alternative git deployment script, in case a GIT deployment target
is supplied (for the specific target system). You can use the following
setting to force git deployment for the LIVE stage, e.g. (command
line):
In the docker container the git deployment will be done in the
/tmp/smui-git-repo path. You need to make sure, that identification is provided to the SMUI docker
environment:
The following example illustrates how to configure SMUI and pass host’s identity:
docker run \
...
-v ~/.ssh/id_rsa:/smui/.ssh/id_rsa \
-v ~/.gitconfig:/home/smui/.gitconfig \
...
-e SMUI_2SOLR_DST_CP_FILE_TO="GIT" \
-e SMUI_DEPLOYMENT_GIT_REPO_URL="ssh://git@repo-host.tld/smui_rulestxt_repo.git" \
...
querqy/smui
Note
When working with remote git locations, it might be necessary to also add your git repo host to SMUI’s
/home/smui/.ssh/known_hosts.As of v3.11.5 only deployment of the common rules.txt file is supported (neither decompound- nor replace-rules.txt files). Support for that might be added in future releases.
Currently only git deployment to the LIVE instance is possible.
Creating initial data¶
After the first startup of SMUI, initial data can be inserted. SMUI supports a REST interface to PUT admin entities (like the following) into the database. This initial data configures Solr collections.
Solr Collections to maintain Search Management rules for¶
There must exist a minimum of one Solr collection (or
querqy/rules.txt deployment target), that Search Management rules
are maintained for. This must be created before the application can be
used. Example curl (relative to localhost:9000):
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"name":"core_name1", "description":"Solr Search Index/Core #1"}' http://localhost:9000/api/v1/solr-index
[...]
NOTE: solr-index/name (in this case core_name1) will be used as
the name of the Solr core, when performing a Core Reload (see
smui2solr.sh).
Initial Solr fields¶
Optional. Example curl (relative to localhost:9000):
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"name":"solr-field-1"}' http://localhost:9000/api/v1/{SOLR_INDEX_ID}/suggested-solr-field
[...]
Where solr-field-1 refers to the field in your configured Solr
schema you would like to make addressable to the Search Manager.
{SOLR_INDEX_ID} refers to the index ID created by the solr-index
call above.
Refresh Browser window and you should be ready to go.